Amidst the diversity of human cultures and belief systems, the world’s five major religions—Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam—offer profound insights into the human condition. Despite their apparent differences in rituals, scriptures, and theological doctrines, these religions share fundamental commonalities that underscore a shared human quest for understanding and connection.
A Universal Longing for Meaning
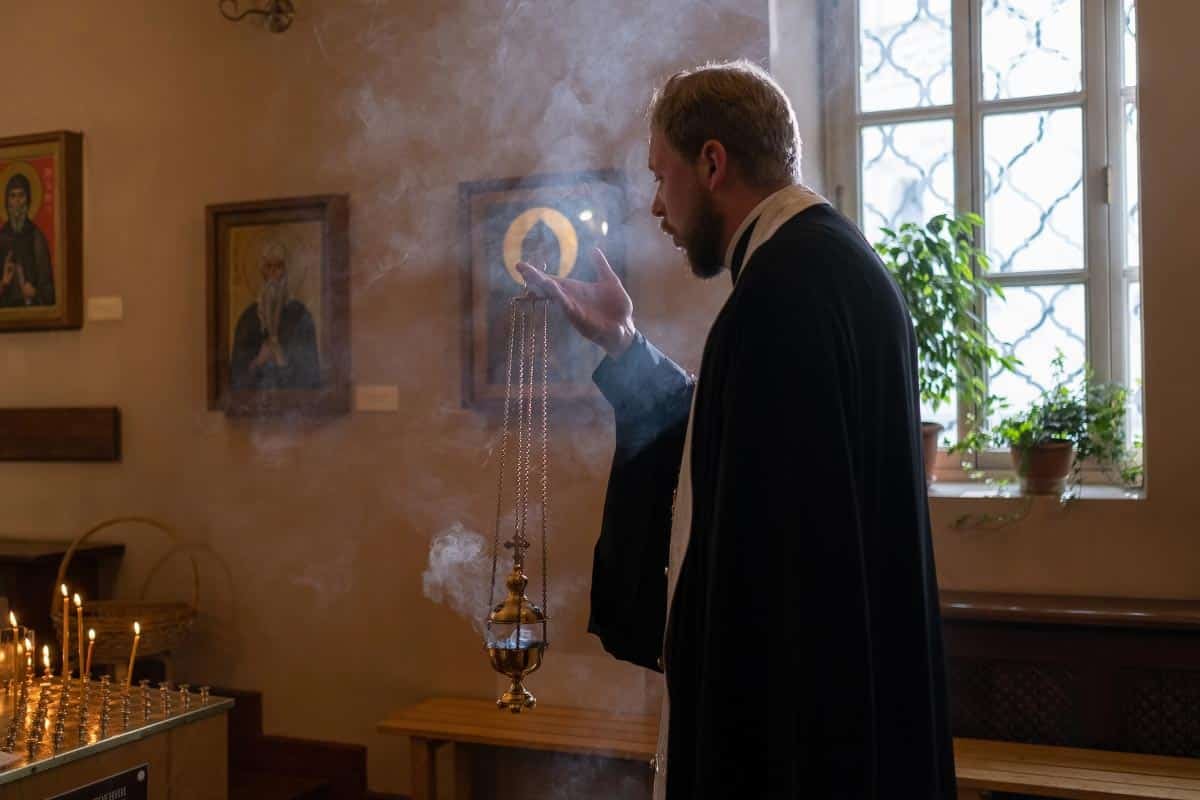

From beliefs in a higher power to ethical frameworks guiding human conduct, from rituals and worship practices to views on the afterlife, these religions resonate with a universal longing for meaning and spiritual fulfillment. In exploring these shared elements, we can see we are far more alike than different – even in how we practice our faith.
Belief in a Higher Power or Divine Principle
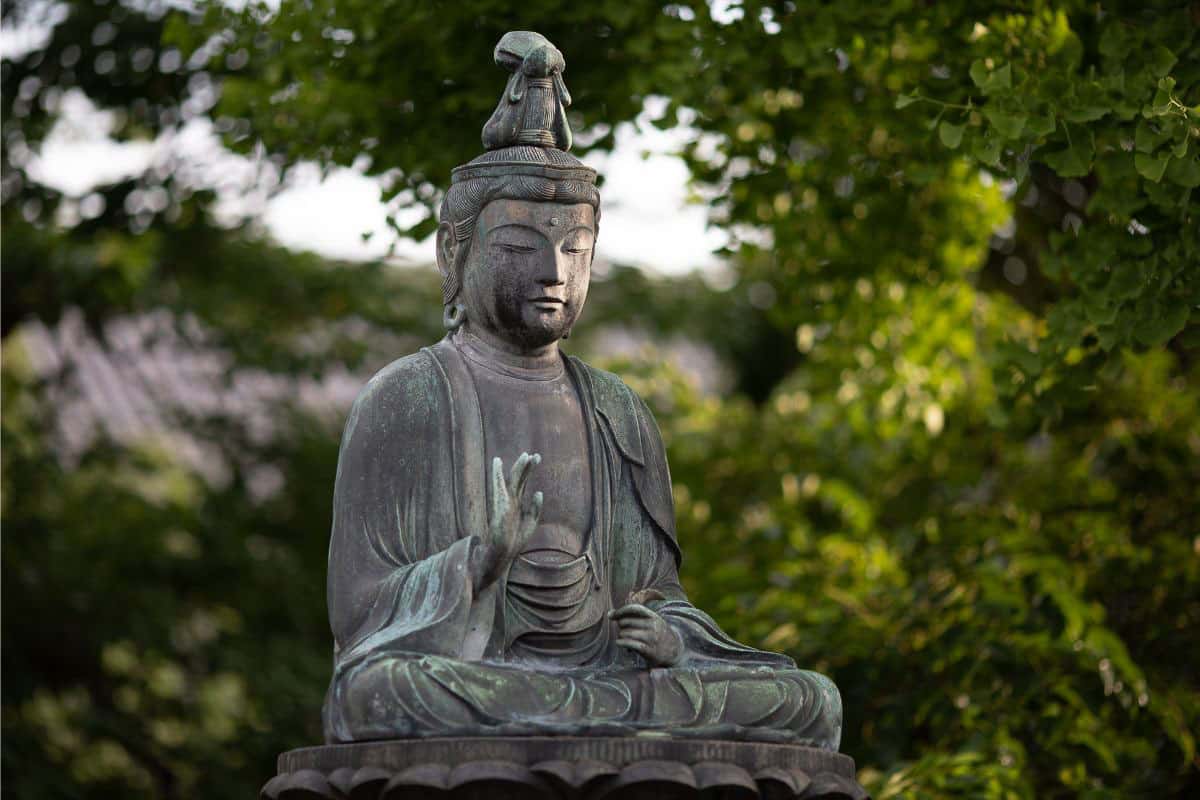

All five religions acknowledge the existence of a divine or higher spiritual reality. Hinduism recognizes a supreme cosmic spirit, Brahman, along with a pantheon of gods. Buddhism, while not theistic in the traditional sense, respects universal laws and sometimes venerates enlightened beings like Buddhas. Judaism, Christianity, and Islam are monotheistic, each worshiping one God.
Ethical Guidelines
Each religion provides a set of ethical guidelines and moral teachings that aim to guide the behavior of its followers. These include principles like compassion, honesty, and justice. The Golden Rule, or the principle of treating others as one would like to be treated, is a concept found in various forms across these religions.
Rituals and Worship
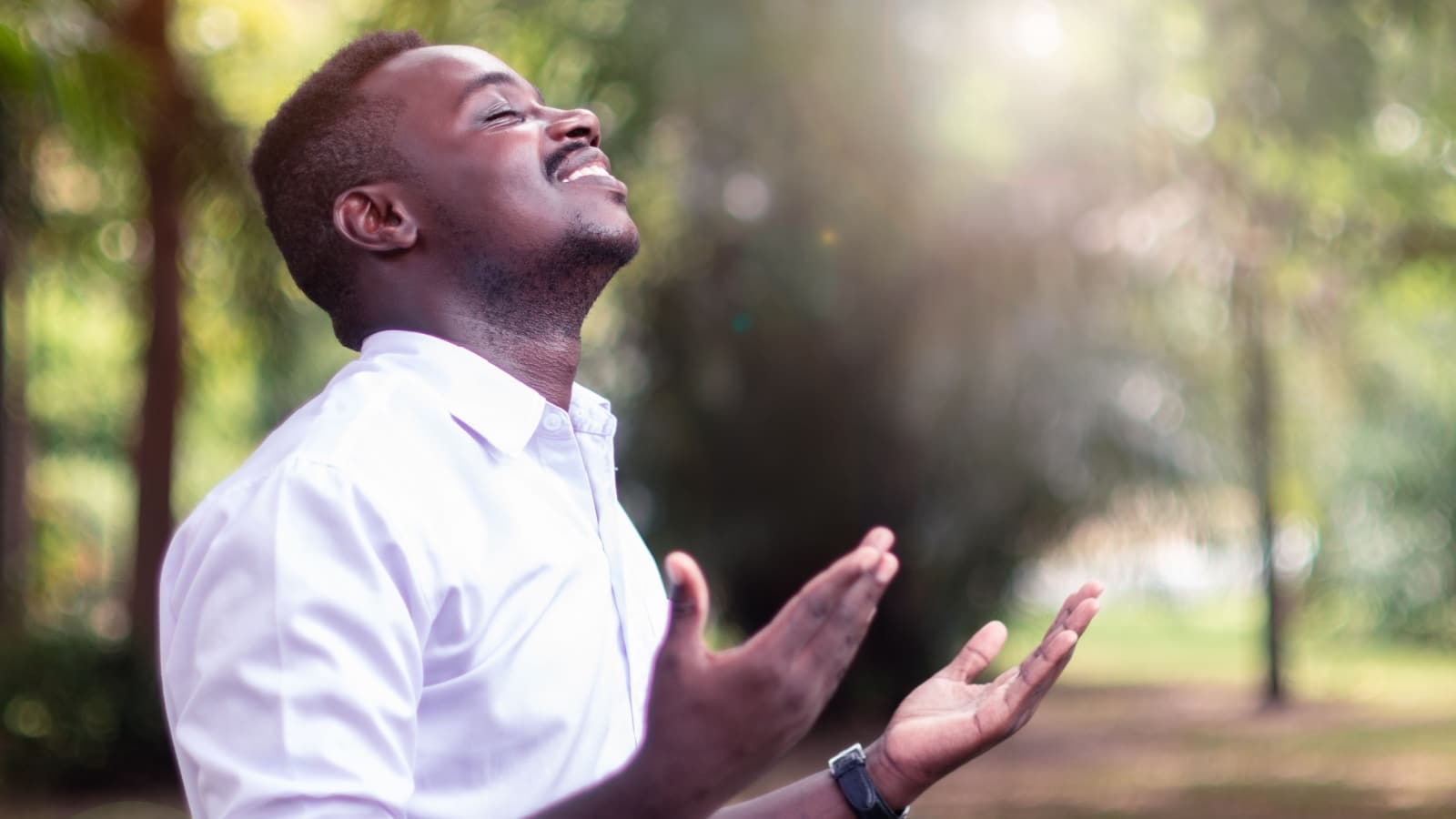

Rituals play a crucial role in all five religions, serving as expressions of faith and devotion. These include prayer, meditation, fasting, and ceremonies. For example, prayer is significant in Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, while meditation is central to Buddhism and Hinduism.
Scriptures and Sacred Texts
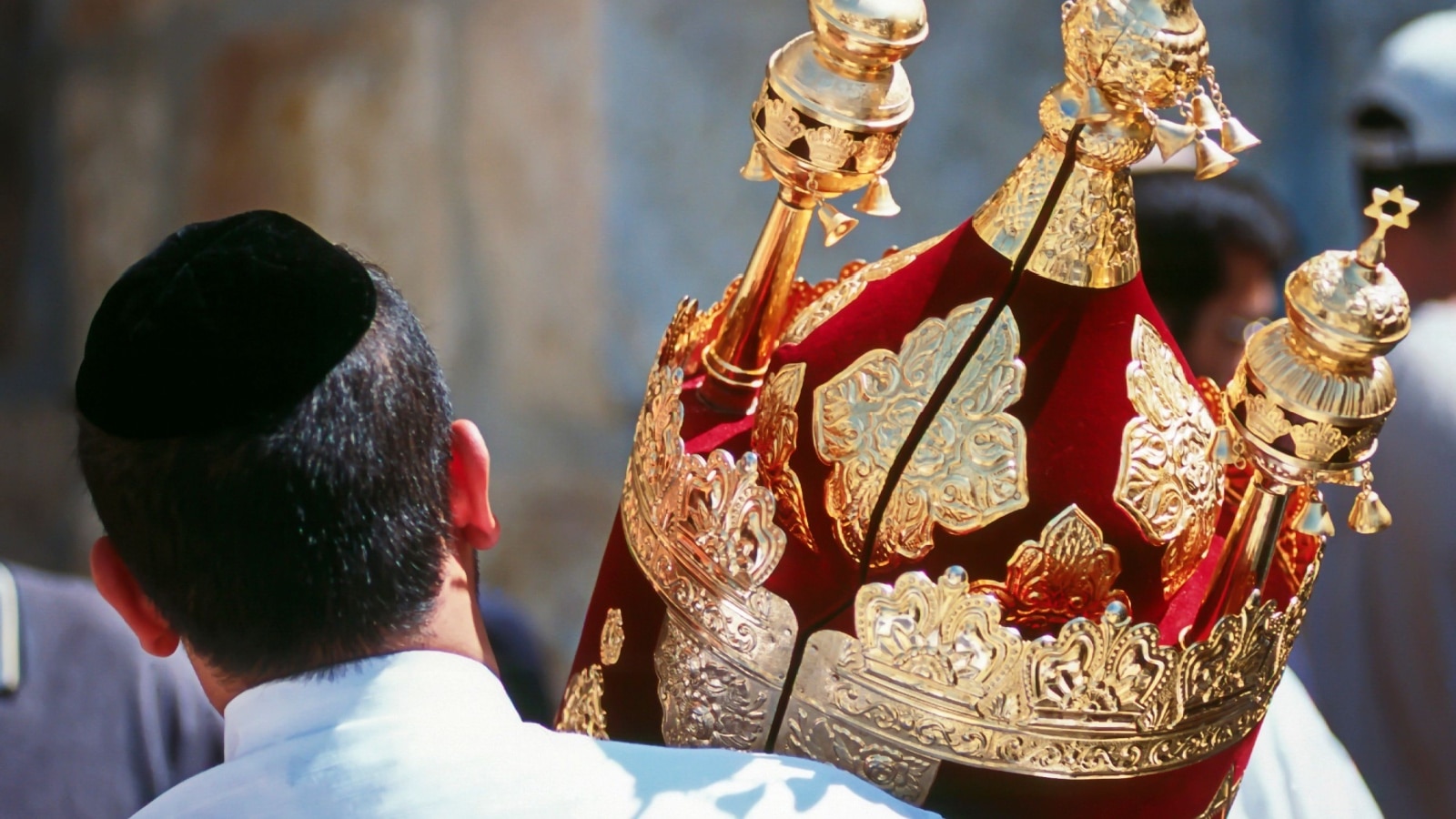

Each religion has its own sacred texts that record the teachings, rituals, and laws central to the faith. Hindus revere texts like the Vedas and the Bhagavad Gita, Buddhists follow the Sutras, Jews the Torah, Christians the Bible, and Muslims the Quran.
Eschatology (Views on Afterlife and Salvation)
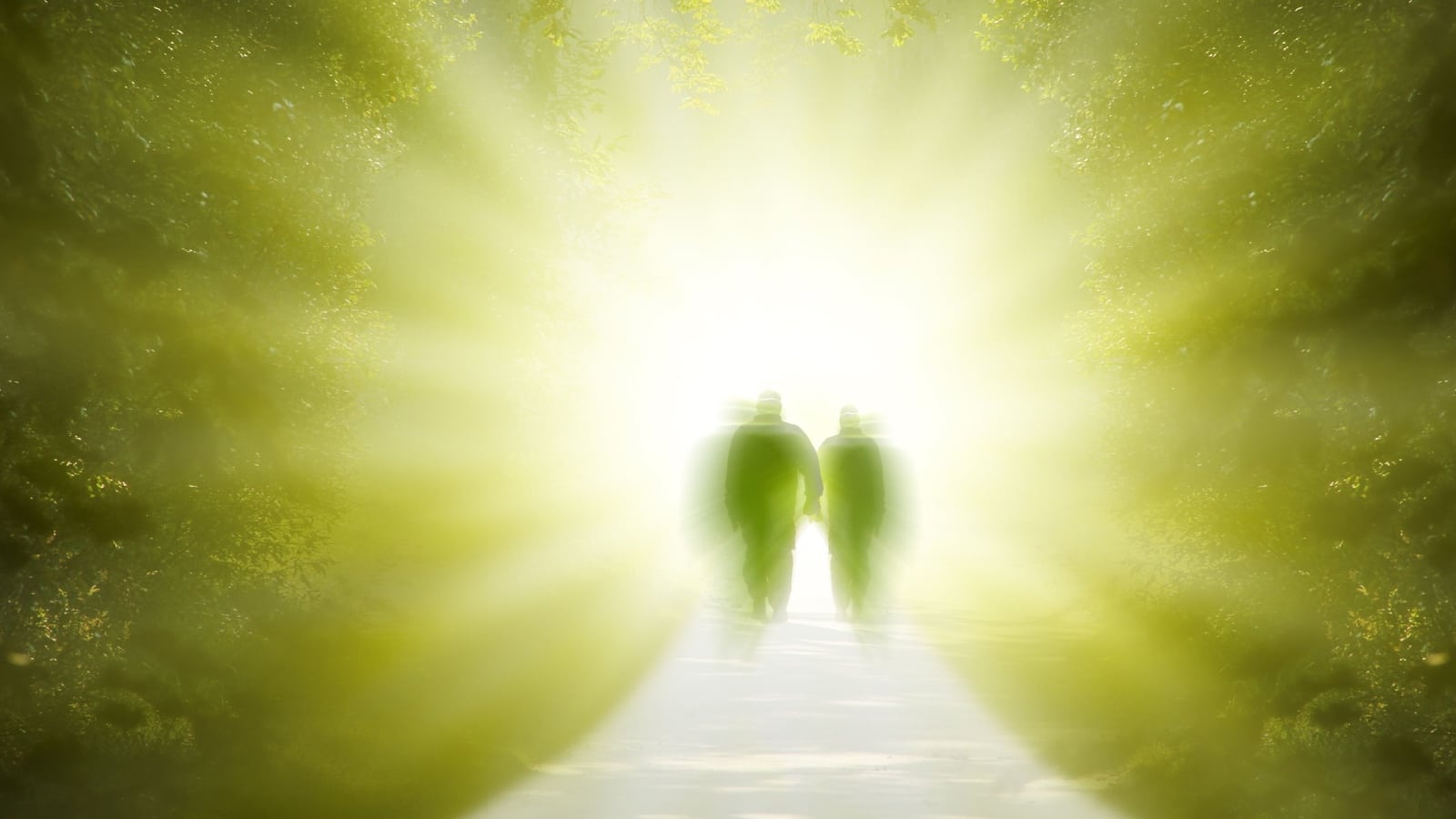

All five religions have beliefs about the afterlife and the path to salvation or liberation. Christianity and Islam, for instance, teach about heaven and hell as final destinations based on moral life conduct. Hinduism and Buddhism discuss liberation (moksha or nirvana) from the cycle of rebirth. Judaism has varied beliefs about the afterlife but generally emphasizes ethical living and the coming of the Messiah.
Community and Social Bonding

Each religion emphasizes the importance of community and collective worship, which strengthens social bonds and provides a support system for followers. This communal aspect is evident in the congregation at mosques, churches, synagogues, temples, and monasteries.
Shared Human Quest For Understanding

These similarities underscore a shared human quest for understanding, meaning, and connection within a larger cosmic framework, despite the diverse ways these religions articulate their beliefs and practices
The Main Differences Between the Five Major Religions

—Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam—can be categorized based on their foundational beliefs, practices, and theological concepts:
Hinduism

– Polytheistic: Hinduism is characterized by a belief in multiple gods and goddesses, each representing various aspects of life and the universe.
– Reincarnation and Karma: Central to Hindu belief is the concept of reincarnation, where the soul is reborn into different lives based on karma, the sum of a person’s actions and their ethical consequences.
– Vedic Texts: Sacred texts such as the Vedas, Upanishads, and the Bhagavad Gita guide the religious practices and philosophies of Hinduism.
Buddhism

– Founded by Siddhartha Gautama (Buddha): Buddhism originated with the teachings of Buddha, who emphasized enlightenment through the Middle Way, avoiding both extreme asceticism and indulgence.
– Four Noble Truths and the Eightfold Path: These form the core of Buddhist teaching, focusing on the nature of suffering, its causes, and the path to its cessation.
– No Central God: Unlike monotheistic religions, Buddhism does not focus on the worship of a god but rather on personal spiritual development and the attainment of a deep insight into the true nature of life.
Judaism

– Monotheistic: Judaism is strictly monotheistic, worshiping one God known as Yahweh or Elohim.
– Covenant and Law: Jews believe in a special covenant with God, with adherence to the laws and commandments set forth in the Torah, which is part of their wider sacred scripture.
– Ethnic and Religious Identity: Judaism combines both an ethnic and a religious identity, which is somewhat unique among the major religions.
Christianity

– Monotheistic: Christians believe in one God, but they uniquely understand God as a Trinity (Father, Son, Holy Spirit).
– Jesus Christ: Christians believe Jesus Christ is the son of God and the savior of humanity whose coming was prophesied in the Old Testament.
– Salvation and Grace: Central to Christian doctrine is the belief in salvation through faith in Jesus Christ and the grace of God.
Islam

– Monotheistic: Muslims believe in one God, Allah, who is omnipotent and omniscient.
– Quran: Muslims follow the Quran, believed to be the literal word of God as revealed to the Prophet Muhammad.
– Five Pillars: The practice of Islam is structured around five pillars which include the declaration of faith, prayer, almsgiving, fasting during Ramadan, and pilgrimage to Mecca.
Takeaway

In examining the foundational beliefs, practices, and theological concepts of Hinduism, Buddhism, Judaism, Christianity, and Islam, we witness both the unity and diversity of human religious expression. While each religion offers unique insights into the nature of existence and the divine, they also converge on essential principles of compassion, moral conduct, and communal worship.
By recognizing these shared values and aspirations, we embrace the richness of our religious heritage and forge connections that transcend religious divides, fostering a deeper sense of unity and understanding in our global community.
Checklist Of 25 Healthy Habits for a Happier Life

In our fast-paced world, prioritizing our health has never been more crucial. Embracing healthy habits can significantly enhance our overall well-being and quality of life. These 25 are our top choices for improving and maintaining oneself during their lifetime. Read: Checklist Of 25 Healthy Habits for a Happier Life







